Command Line Interface(CLI)
What is CLI ?
CLI stands for Command Line Interface. CLI is a text-based interface that allows users to interact with a computer's operating system by entering commands.
Basic CLI commands in linux
cd command
cd means change directory. You invoke it specifying a folder to move into. You can specify a folder name, or an entire path.
Example:
mkdir hello
cd hello # now your in the hello folder
You can use the .. special path to indicate the parent folder:
cd .. #back to the home folder
There is another special path indicator which is ., and indicates the current folder.
mkdir command
mkdir means make directory. mkdir command is used to create a folders.
mkdir fruits # fruits folder is created
You can create multiple folders with one command:
mkdir dogs cars
rmdir command
rmdir means remove directory. rmdir command is used to delete a folders.
mkdir fruits
rmdir fruits # deleting fruits folder
You can also delete multiple folders at once:
mkdir fruits cars
rmdir fruits cars
The folder you delete must be empty.
To delete folders with files in them, we will use rm command which deletes files and folders, using the -rf option:
rm -rf fruits cars
touch command
touch is used to create an empty file.
touch hello # creating empty file with name hello
pwd command
pwd means present working directory. It will print the current folder path.
pwd # print current folder path
ls command
ls command is used to list all the files inside folder.
ls
ls accepts a lot of options. One of my favorite combinations is -al. Try it:
ls -al # list all hidden and long term files

mv command
mv means move, it is used to moves files and directories from one directory to another or renames a files and folders.
touch test
mv pear new_pear
The pear file is now moved to new_pear. This is how you rename files and folders.
cp command
You can copy a file using the cp command:
touch test
cp apple another_apple
To copy folders you need to add the -r option to recursively copy the whole folder contents:
mkdir fruits
cp -r fruits cars
cat command
cat command on linux concatenates files together, cat can also add content to a file.
cat prints a file's content to the standard output:
cat file
You can print the content of multiple files:
cat file1 file2
and using the output redirection operator > you can concatenate the content of multiple files into a new file:
cat file1 file2 > file3
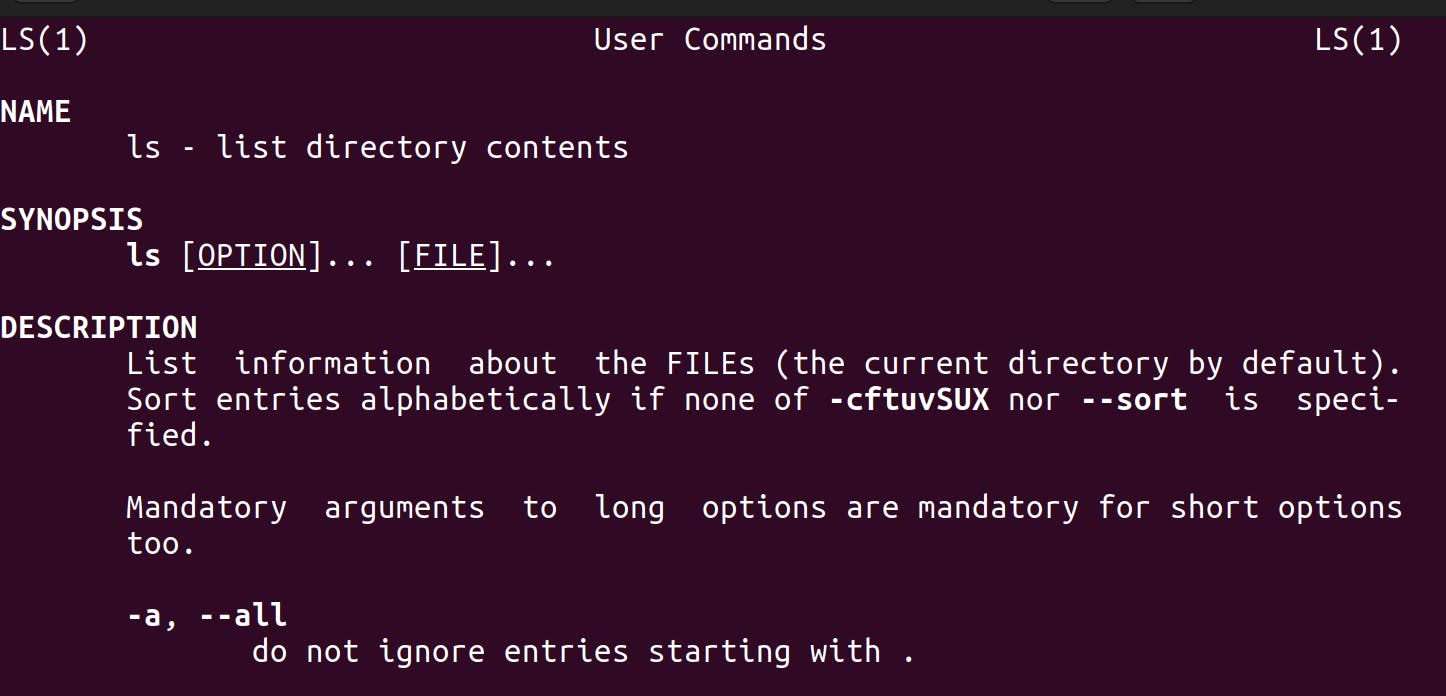
man command
man stands for manual, It is used to display the user manual of any command that we can run on the terminal.
man ls
echo command
echo command prints to the output the argument passed to it.
echo "hello"
will print hello to the terminal.
We can append the output to a file:
echo "hello" >> output.txt
open command
The open command lets you open a file using this syntax:
open test # open the test file
I use it all the time to open the current directory:
open .
nano command
nano is a beginner friendly editor.
Run it using nano <filename>.
You can directly type characters into the file without worrying about modes.
You can quit without editing using ctrl-X. If you edited the file buffer, the editor will ask you for confirmation and you can save the edits, or discard them.
The help at the bottom shows you the keyboard commands that let you work with the file:
chmod command
chmod stands for change mode, it is used to we can set 3 permissions: read, write, and execute.

The first letter indicates the type of file:
-means it's a normal filedmeans it's a directorylmeans it's a link
Then you have 3 sets of values:
The first set represents the permissions of the owner of the file
The second set represents the permissions of the members of the group the file is associated to
The third set represents the permissions of the everyone else
chmodcan be used in 2 ways. The first is using symbolic arguments, the second is using numeric arguments.1. symbolic argumnts:
You type
chmodfollowed by a space, and a letter:astands for allustands for usergstands for groupostands for otherschmod a+r filename #everyone can now read chmod a+rw filename #everyone can now read and write chmod o-rwx filename #others (not the owner, not in the same group of the file) cannot read, write or execute the file- numeric arguments:
This gives us 4 combinations:
0no permissions1can execute2can write3can write, execute4can read5can read, execute6can read, write7can read, write and execute
We use them in pairs of 3, to set the permissions of all the 3 groups altogether:
chmod 777 filename
chmod 755 filename
chmod 644 filename